homozygous dominant What percentage of our genetic makeup is similar to other people
Probability of Inheritance
The value of studying genetics is in agreement how nosotros tin can predict the likelihood of inheriting particular traits. This tin can help establish and animal breeders in developing varieties that take more desirable qualities. Information technology tin also assistance people explain and predict patterns of inheritance in family lines.One of the easiest ways to summate the mathematical probability of inheriting a specific trait was invented by an early on 20th century English geneticist named Reginald Punnett
. His technique employs what we at present phone call a Punnett square . This is a simple graphical way of discovering all of the potential combinations of genotypes that tin occur in children, given the genotypes of their parents. It as well shows us the odds of each of the offspring genotypes occurring.
Setting up and using a Punnett square is quite simple one time you lot empathise how it works. You begin by drawing a grid of perpendicular lines:
Next, yous put the genotype of one parent across the top and that of the other parent down the left side. For example, if parent pea plant genotypes were YY and GG respectively, the setup would exist:
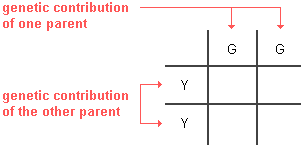
Note that simply one letter goes in each box for the parents. Information technology does not matter which parent is on the side or the superlative of the Punnett square.
Next, all you have to practice is fill in the boxes by copying the row and column-caput letters across or down into the empty squares. This gives us the predicted frequency of all of the potential genotypes among the offspring each time reproduction occurs.
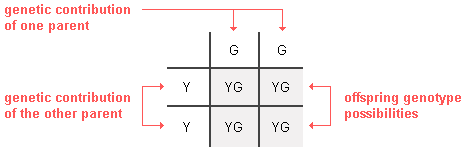
In this example, 100% of the offspring will likely be heterozygous (YG). Since the Y (yellow) allele is dominant over the G (light-green) allele for pea plants, 100% of the YG offspring will take a yellow phenotype, as Mendel observed in his breeding experiments.
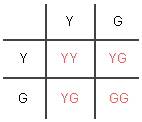
In another instance (shown beneath), if the parent plants both have heterozygous (YG) genotypes, there will exist 25% YY, 50% YG, and 25% GG offspring on boilerplate. These percentages are determined based on the fact that each of the 4 offspring boxes in a Punnett square is 25% (ane out of iv). Every bit to phenotypes, 75% will be Y and only 25% will exist G. These will be the odds every fourth dimension a new offspring is conceived by parents with YG genotypes.
An offspring'due south genotype is the result of the combination of genes in the sex cells or gametes (sperm and ova) that came together in its conception. One sex activity cell came from each parent. Sex cells normally simply have one copy of the gene for each trait (eastward.g., ane copy of the Y or G form of the factor in the example above). Each of the ii Punnett square boxes in which the parent genes for a trait are placed (across the top or on the left side) really represents ane of the two possible genotypes for a parent sex activity cell. Which of the two parental copies of a factor is inherited depends on which sex cell is inherited--it is a affair of chance. By placing each of the two copies in its own box has the issue of giving it a l% run a risk of beingness inherited.
If you are not yet clear nearly how to make a Punnett Square and interpret its result, have the time to endeavour to figure it out before going on.
Are Punnett Squares Just Academic Games?Why is it important for yous to know about Punnett squares? The respond is that they can be used every bit predictive tools when because having children. Let us assume, for instance, that both you and your mate are carriers for a specially unpleasant genetically inherited illness such as cystic fibrosis
. Of course, you are worried about whether your children volition be healthy and normal. For this instance, let us ascertain "A" every bit being the dominant normal allele and "a" as the recessive abnormal 1 that is responsible for cystic fibrosis. As carriers, you and your mate are both heterozygous (Aa). This disease simply afflicts those who are homozygous recessive (aa). The Punnett square beneath makes it articulate that at each birth, there volition be a 25% gamble of yous having a normal homozygous (AA) child, a 50% chance of a healthy heterozygous (Aa) carrier kid like yous and your mate, and a 25% chance of a homozygous recessive (aa) child who probably will eventually die from this condition.
If a carrier (Aa) for such a recessive illness mates with someone who has it (aa), the likelihood of their children also inheriting the condition is far greater (as shown below). On average, half of the children will be heterozygous (Aa) and, therefore, carriers. The remaining one-half volition inherit 2 recessive alleles (aa) and develop the disease.
It is likely that every ane of us is a carrier for a large number of recessive alleles. Some of these alleles tin crusade life-threatening defects if they are inherited from both parents. In improver to cystic fibrosis, albinism, and beta-thalassemia are recessive disorders.
Some disorders are caused by dominant alleles for genes. Inheriting just 1 copy of such a dominant allele will cause the disorder. This is the case with Huntington affliction, achondroplastic dwarfism, and polydactyly. People who are heterozygous (Aa) are non healthy carriers. They have the disorder just like homozygous ascendant (AA) individuals.
Punnett squares are standard tools used by genetic counselors. Theoretically, the likelihood of inheriting many traits, including useful ones, tin exist predicted using them. It is also possible to construct squares for more than one trait at a time. Still, some traits are not inherited with the simple mathematical probability suggested here. We will explore some of these exceptions in the next department of the tutorial.
Copyright � 1997-2012 by Dennis O'Neil. All rights reserved.
illustration credits
Source: https://www2.palomar.edu/anthro/mendel/mendel_2.htm
0 Response to "homozygous dominant What percentage of our genetic makeup is similar to other people"
Post a Comment